Multiple Sclerosis
Multiple Sclerosis Protocol
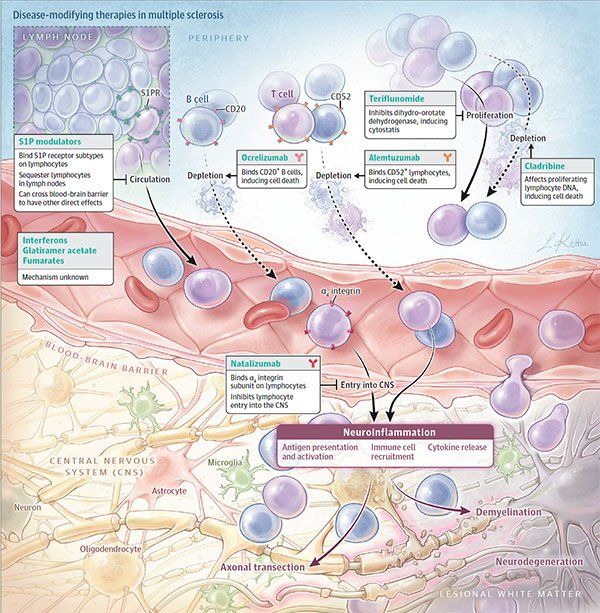
Fig.1. (JAMA. 2021;325(8):765-779. doi:10.1001/jama.2020.26858)
IVHealthClub Treatment protocol for Multiple Sclerosis
- Decrease oxidative damage
- Decrease inflammation
- Improve gut microbiome
- support immune system to prevent secondary infections
- Neuro drip 500 mL weekly for 8 weeks
- NAD drip 250 mg weekly for 8 weeks then switch to NAD spray indefinite
- High dose vitamin D program for 4 weeks
- High dose niacin indefinite
- High dose Melatonin indefinite
- IV glutathione weekly
- diet modification gluten free etc.
Vitamin D replacement
Vitamin D deficiency is associated with an increased risk of multiple sclerosis (MS), a chronic immune‐mediated demyelinating disease of the central nervous system.
The main mechanisms of action of vitamin D in MS appear to be immunomodulatory, involving the various categories of T and B lymphocytes in the general immune system, but neuroprotector and neurotrophic mechanisms could also be exerted at the central nervous system level.
According to study by s. Simpson Jr higher 25-OH-D levels were associated with a reduced hazard of relapse. This occurred in a dose-dependent linear fashion, with each 10 nmol/l increase in 25-OH-D resulting in up to a 12% reduction in risk of relapse.
Ann Neurol . 2010 Aug;68(2):193-203. doi: 10.1002/ana.22043.
High dose Niacin
In the central nervous system, vitamin B3 (Niacin) has long been recognized as a key mediator of neuronal development and survival, especially during oxidative stress conditions, and this effect is achieved via multiple mechanisms.
J Cereb Blood Flow Metab . 2004 Jul;24(7):728-43. doi: 10.1097/01.WCB.0000122746.72175.0E.
MS patients are now known to be deficient in niacin. High dose niacin can be expected to be beneficial in the treatment of MS, and positive reports have previously been reported for high dose niacin administration to MS patients.
http://orthomolecular.org/resources/omns/v14n15.shtml
At higher concentrations, they display separate additional pharmacological activities, ranging from anti-dyslipidemic to anti-inflammatory action.
Regardless the type of brain injury, greater beneficial effects have been observed when vitamin B3 was administrated in combination with other “natural compounds” Selenium is one of those.
Crit Care Med . 2018 Aug;46(8):e788-e796. doi: 10.1097/CCM.0000000000003198.
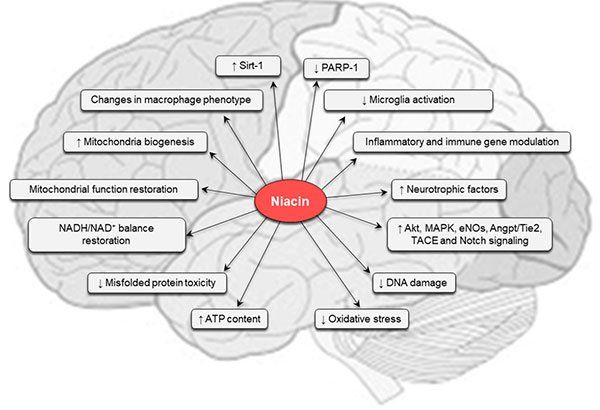
by W. Todd Penberthy and Robert G. Smith
Because nutritional treatments are effective and very safe, they should be tried first before drugs. Elimination of gluten and dairy (milk) can lead to dramatically positive benefits for some. This approach can be required and has been effective for many patients and deserves much more consideration as a standard part of treatment for preventing neurodegeneration in MS attacks.
The single most important requirement for reversal of multiple sclerosis is the elimination of gluten and restoration of a healthy microbiome.
The elimination of dairy, the second most common food allergy, can be critical too.
There are two diets some experts recommend:
Wahls protocol:
The diet is a version of the Paleolithic (Paleo) diet. On the Wahls Protocol, Eat lots of: Meat and fish Vegetables, especially green, leafy ones Brightly colored fruit, like berries Fat from animal and plant sources, especially omega-3 fatty acids.
Do not eat: Dairy products and eggs Grains (including wheat, rice, and oatmeal) Legumes (beans and lentils)
Nightshade vegetables, which include tomatoes, eggplant, potatoes, and peppers and Sugar.
the Swank diet:
basically, is a low-fat diet
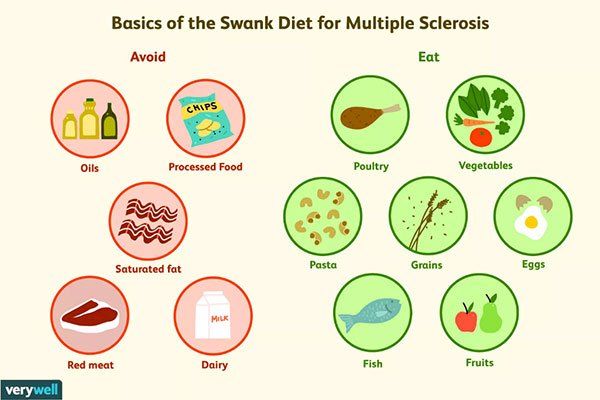
Foods
*No gluten; minimal dairy (grass-fed butter and eggs are OK as long as no egg allergy)
3 cups leafy greens (arugula, collards, kale, etc.)
3 cups colorful (beets, carrots, berries)
3 cups sulfur-rich (broccoli, cauliflower, cabbage, kale, collards, Brussels sprouts)
Least expensive way is homegrown non-certified organic; most convenient way is frozen
Ideally, half your body weight in ounces of water daily, e.g., 80oz water for 160lbs; no fluoride and little chlorine.
NAD Treatments for Multiple Sclerosis
Due to the multiplicity of NAD-dependent biological events, which lead to NAD degradation, cells need to replenish their intracellular NAD content within a few hours. Neurons are particularly exquisitely susceptible to NAD deficiency induced cell death.
In mammalian cells, NAD can be synthesized in two pathways from multiple precursors, including tryptophan, nicotinic acid, nicotinamide, and nicotinamide riboside (NmR), via multiple enzymatic steps.
NAD can be synthesized by two pathways:
- de novo synthesis from tryptophan. For the de novo pathway to be completed it is necessary to have adequate riboflavin (vitamin B2), pyridoxal phosphate (vitamin B6), and ascorbate (vitamin C).
- NAD can also be synthesized from three different essential non-amino acid precursors in the diet: nicotinic acid (NA), nicotinamide (NAM), and nicotinamide riboside (NAMR).
It should be realized that not every cell is capable of converting each precursor to NAD at all times although NAD is essential to survival.
Curr Pharm Des. 2009; 15(1): 64–99.
Experiments suggest that the tryptophan de novo biosynthesis pathway is not efficient enough to provide neuroprotection.
J Neurosci . 2006 Aug 16;26(33):8484-91. doi: 10.1523/JNEUROSCI.2320-06.2006.
Under conditions of NAD deficiency, neurons are exceptionally vulnerable to the degeneration characteristic of MS. Exogenous application of nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD) can protect axons of cultured dorsal root ganglion (DRG) neurons from degeneration caused by mechanical or neurotoxic injury.
Collectively, experimental observations support the idea that by increasing NAD, we may be able to prevent or reduce the effects of MS pathogenesis. this loss of available NAD precursor can be partially rescued either by administrating pharmacological doses of nicotinamide.
Once the body has enough NAD to perform most of its desired chemistry, then one the next co-factors to become rate-limiting for performing of endogenous biochemistry is pyridoxal phosphate (vitamin B6) or cobalamin (vitamin B12). This makes sense given that NAD is perhaps followed by pyridoxal phosphate in the shear total number of known reactions requiring these co-factors respectively. Furthermore, it is well known that deficiencies of cobalamin lead to demyelination and such deficiencies have on occasion been observed in MS.
Nicotinamide riboside was only recently discovered in 2004 Of potentially great clinical therapeutic significance nicotinamide riboside is distinguished as the only NAD precursor capable of providing NAD directly to neurons.