Parkinson's disease
Parkinson’s disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive disorder characterized by degeneration of dopaminergic neurons within the substantia nigra, whose main hallmarks are abnormal aggregation of the alpha-synuclein protein, inhibition of mitochondrial respiratory complex 1, oxidative stress and neuroinflammation.
Pesticide, herbicide, and heavy metal exposures are linked to an increased risk of Parkinson disease in some epidemiologic studies.
At cellular level in Parkinson’s, increased NK cells, IL -1B, IL 6, TNF alpha detected in the CSF; also augmented expression of both CD14 and TLR4 in the substantia nigra demonstrated.
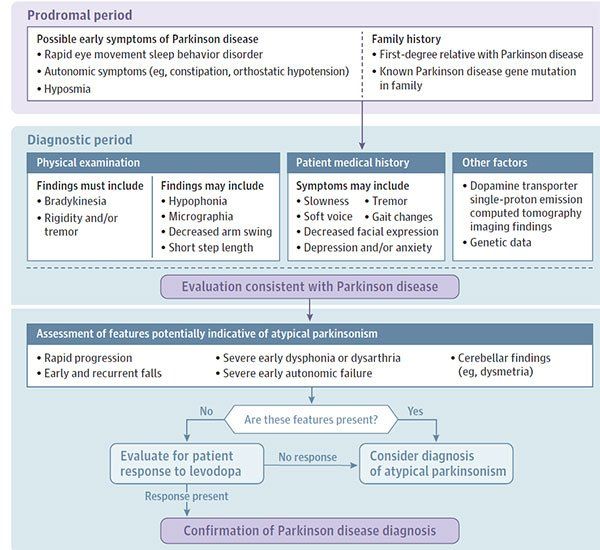
Fig 1 Proposed Approach to Diagnosing Parkinson Disease (JAMA. 2020 Feb 11;323(6):548-560. doi: 10.1001/jama.2019.22360.)
Parkinson’s disease treatment depends on symptoms only, not focused on prevention for further neuron damage. Motor symptoms treatments are primarily dopamine based.
More than 40% of individuals treated with oral dopamine agonists (ropinirole, pramipexole) experience impulse control disorders (eg, gambling, compulsive spending, abnormal sexual and eating behaviors, compulsive medication use, hobbyism).
Individuals who discontinue use of dopamine agonists, often due to impulse control disorders, experience withdrawal symptoms (eg, anxiety, panic attacks, irritability, diaphoresis, pain, drug cravings) 15% to 20% of the time. Due to this, sometimes the dopamine agonist cannot be discontinued despite serious associated adverse events such as impulse control disorders.
In IVHealthclub, we offer various intravenous vitamin and mineral combinations which directly work on inflammation and oxidative stress in central nervous system.
IVHealthClub Treatment protocol for Parkinson’s disease
First step:
Focused on preventing neurotoxicity associated with mitochondrial defects. Prevent further neuron damage, evaluate, and treat environmental factors such as toxin or heavy metal exposure.
- Evaluate Heavy metal toxicity and treatment with chelation protocol (can be up to 20 weeks).
- High dose IV Glutathione 2000 mg twice a week for 8 weeks
- Neuro drip 500 mL weekly for 8 weeks
Second step:
NAD Treatments
NAD+ levels, indeed, fall in patients with PD and, conversely, increasing niacin intake can increase dopamine synthesis in the striatum and restore optimal NAD+/NADH ratio needed for the activity of mitochondrial complex.
NAD supplementation or inactivation of NAD-consuming enzymes [like PARP-1, a poly(ADP-ribose) polymerase involved in DNA repair]rescue mitochondrial defects and protect neurons against degeneration, in familial forms of PD characterized by mutations in the pink1 gene; this finding suggests that neurotoxicity associated with mitochondrial defects may be prevented by modulating NAD+
Biol Open . 2017 Feb 15;6(2):141-147. doi: 10.1242/bio.022186.
- First 8-week treatment with IV NAD followed by nasal NAD spray indefinite.
Third step:
Maintenance treatments
1. High dose Niacin (optimal levels of vitamin B3 are needed for reducing oxidative stress and neuroinflammation in patient with Parkinson’s)
2. Green Tea
3. Resveratrol
4. Acetvl L-carnitine and polyphenols ( have recently been demonstrated to be neuroprotective through the activation of hormetic pathways, including vitagenes)
Biofactors . Mar-Apr 2009;35(2):146-60. doi: 10.1002/biof.22.
5. Melatonin - upregulation of vitagenes (the brain overcomes oxidative stress by inducing the expression of vitagenes)
6. Curcumin (decreases Quinolinic acid and kynurenine)
Call us today to get a FREE consultation on our IV treatments.
513-507-9677